Claim Check
The Claim Check from the EIP patterns allows you to replace message content with a claim check (a unique key), which can be used to retrieve the message content at a later time.
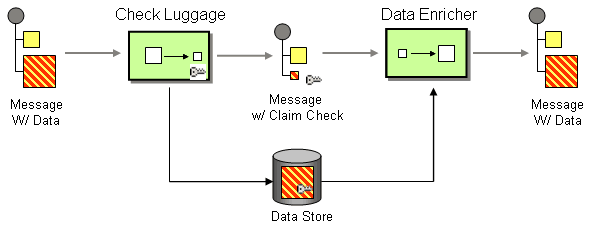
It can also be useful in situations where you cannot trust the information with an outside party; in this case, you can use the Claim Check to hide the sensitive portions of data.
| The Camel implementation of this EIP pattern stores the message content temporarily in an internal memory store. |
The Claim Check eip supports 6 options, which are listed below.
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
description | Sets the description of this node. | String | |
disabled | Whether to disable this EIP from the route during build time. Once an EIP has been disabled then it cannot be enabled later at runtime. | false | Boolean |
operation | The claim check operation to use. The following operations are supported: Get - Gets (does not remove) the claim check by the given key. GetAndRemove - Gets and removes the claim check by the given key. Set - Sets a new (will override if key already exists) claim check with the given key. Push - Sets a new claim check on the stack (does not use key). Pop - Gets the latest claim check from the stack (does not use key). Enum values:
| ClaimCheckOperation | |
key | To use a specific key for claim check id (for dynamic keys use simple language syntax as the key). | String | |
filter | Specify a filter to control what data gets merged data back from the claim check repository. The following syntax is supported: body - to aggregate the message body attachments - to aggregate all the message attachments headers - to aggregate all the message headers header:pattern - to aggregate all the message headers that matches the pattern. The following pattern rules are applied in this order: exact match, returns true wildcard match (pattern ends with a and the name starts with the pattern), returns true regular expression match, returns true otherwise returns false You can specify multiple rules separated by comma. For example, the following includes the message body and all headers starting with foo: body,header:foo. The syntax supports the following prefixes which can be used to specify include,exclude, or remove - to include (which is the default mode) - - to exclude (exclude takes precedence over include) — - to remove (remove takes precedence) For example to exclude a header name foo, and remove all headers starting with bar, -header:foo,--headers:bar Note you cannot have both include and exclude header:pattern at the same time. | String | |
aggregationStrategy | To use a custom AggregationStrategy instead of the default implementation. Notice you cannot use both custom aggregation strategy and configure data at the same time. | AggregationStrategy | |
aggregationStrategyMethodName | This option can be used to explicit declare the method name to use, when using POJOs as the AggregationStrategy. | String |
Claim Check Operation
When using this EIP, you must specify the operation to use which can be of the following:
-
Get: Gets (does not remove) the claim check by the given key. -
GetAndRemove: Gets and removes the claim check by the given key. -
Set: Sets a new (will override if key already exists) claim check with the given key. -
Push: Sets a new claim check on the stack (does not use key). -
Pop: Gets the latest claim check from the stack (does not use key).
When using the Get, GetAndRemove, or Set operation you must specify a key. These operations will then store and retrieve the data using this key. You can use this to store multiple data in different keys.
The Push and Pop operations do not use a key but stores the data in a stack structure.
Merging data using get or pop operation
The Get, GetAndRemove and Pop operations will claim data back from the claim check repository. The data is then merged with the current data on the exchange. This is done with an AggregationStrategy. The default strategy uses the filter option to easily specify what data to merge back.
The filter option takes a String value with the following syntax:
-
body: to aggregate the message body. -
attachments: to aggregate all the message attachments. -
headers: to aggregate all the message headers. -
header:pattern: to aggregate all the message headers that match the pattern.
The pattern rule supports wildcards and regular expressions:
-
wildcard match (pattern ends with a
*, and the name starts with the pattern) -
regular expression match
You can specify multiple rules separated by comma.
Basic filter examples
For example, to include the message body and all headers starting with foo:
body,header:foo*To only merge back the message body:
bodyTo only merge back the message attachments:
attachmentsTo only merge back headers:
headersTo only merge back a header name foo:
header:fooIf the filter rule is specified as empty or as wildcard, then everything is merged.
Notice that when merging back data, any data in the Message that is not overwritten is preserved.
Filtering with include and exclude patterns
The syntax also supports the following prefixes which can be used to specify include, exclude, or remove patterns:
-
+to include (which is the default mode) -
-to exclude (exclude takes precedence over include) -
--to remove (remove takes precedence)
For example, to skip the message body, and merge back everything else
-bodyOr to skip the message header foo and merge back everything else
-header:fooYou can also remove headers when merging data back. For example, to remove all headers starting with bar:
--headers:bar*Note you cannot have both include (+) and exclude (-) header:pattern at the same time.
Dynamic keys
The claim check keys are static, but you can use the simple language syntax to define dynamic keys. For example, to use a header from the message named myKey:
from("direct:start")
.to("mock:a")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Set, "${header.myKey}")
.transform().constant("Bye World")
.to("mock:b")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Get, "${header.myKey}")
.to("mock:c")
.transform().constant("Hi World")
.to("mock:d")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Get, "${header.myKey}")
.to("mock:e");Example
The following example shows the Push and Pop operations in action:
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("direct:start")
.to("mock:a")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Push)
.transform().constant("Bye World")
.to("mock:b")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Pop)
.to("mock:c");<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<to uri="mock:a"/>
<claimCheck operation="Push"/>
<transform>
<constant>Bye World</constant>
</transform>
<to uri="mock:b"/>
<claimCheck operation="Pop"/>
<to uri="mock:c"/>
</route>- from:
uri: direct:start
steps:
- to: mock:a
- claimCheck:
operation: Push
- transform:
expression:
constant: Bye World
- to:
uri: mock:b
- claimCheck:
operation: Pop
- to:
uri: mock:cIn the above example, imagine message body from the beginning is Hello World. That data is pushed on the stack of the Claim Check EIP. Then the message body is transformed to Bye World, which is what mock:b endpoint receives. When we Pop from the Claim Check EIP, the original message body is retrieved and merged back, so mock:c will retrieve the message body with Hello World.
Here is an example using Get and Set operations, which uses the key foo:
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("direct:start")
.to("mock:a")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Set, "foo")
.transform().constant("Bye World")
.to("mock:b")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Get, "foo")
.to("mock:c")
.transform().constant("Hi World")
.to("mock:d")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Get, "foo")
.to("mock:e");<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<to uri="mock:a"/>
<claimCheck operation="Set" key="foo"/>
<transform>
<constant>Bye World</constant>
</transform>
<to uri="mock:b"/>
<claimCheck operation="Get" key="foo"/>
<to uri="mock:c"/>
<transform>
<constant>Hi World</constant>
</transform>
<to uri="mock:d"/>
<claimCheck operation="Get" key="foo"/>
<to uri="mock:e"/>
</route>- from:
uri: direct:start
steps:
- to: mock:a
- claimCheck:
operation: Set
key: foo
- transform:
expression:
constant: Bye World
- to:
uri: mock:b
- claimCheck:
operation: Get
key: foo
- to:
uri: mock:c
- transform:
expression:
constant: Hi World
- to:
uri: mock:d
- claimCheck:
operation: Get
key: foo
- to:
uri: mock:eNotice how we can Get the same data twice using the Get operation as it will not remove the data. If you only want to get the data once, you can use GetAndRemove.
The last example shows how to use the filter option where we only want to get back header named foo or bar:
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("direct:start")
.to("mock:a")
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Push)
.transform().constant("Bye World")
.setHeader("foo", constant(456))
.removeHeader("bar")
.to("mock:b")
// only merge in the message headers foo or bar
.claimCheck(ClaimCheckOperation.Pop, null, "header:(foo|bar)")
.to("mock:c");<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<to uri="mock:a"/>
<claimCheck operation="Push"/>
<transform>
<constant>Bye World</constant>
</transform>
<setHeader name="foo">
<constant>456</constant>
</setHeader>
<removeHeader headerName="bar"/>
<to uri="mock:b"/>
<!-- only merge in the message headers foo or bar -->
<claimCheck operation="Pop" filter="header:(foo|bar)"/>
<to uri="mock:c"/>
</route>- from:
uri: direct:start
steps:
- to:
uri: mock:a
- claimCheck:
operation: Push
- transform:
expression:
constant: ByeWorld
- setHeader:
name: foo
expression:
constant: 456
- removeHeader:
name: bar
- to:
uri: mock:b
- claimCheck:
operation: Pop
filter: "header:(foo|bar)"
- to:
uri: mock:c